The functions of RBI (Reserve Bank of India) are as important as the Ministry of Finance. RBI is not just a bank, it bank of banks. When I was a child I always wanted to open a bank account in the Reserve Bank of India. The enormity and magnitude of its office building itself used to tell me that this bank is the best.
But as I grew up I began to realize that even my father (whom I considered my epitome) did not have an account in this bank. I even never heard him talking about the reserve bank of India.
But I used to hear the name of the reserve bank of India on television news channels. A doubt came to my mind whether this is a bank at all. I asked a question to my father and in simple terms, he explained to me that “The Reserve Bank of India is a Banker to the Government of India and all India Banks
In nutshell, I could make it that RBI is possibly the BOSS of all banks in India. As a common man saves and lends money from banks like SBI, ICICI, HDFC, etc, in the same way, these banks save and lend money from the reserve bank of India“. But this question always kept on nudging my head about what can be other functions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Suggested Reading: India’s Bitcoin (Digital Currency)
Functions of RBI
- Monetary Authority: The main function of RBI is formulating and implementing the monetary policies of India. Creating and balance between “Price stability” and “future economic growth” is the main challenge of RBI as a monetary authority. Read more on the monetary authority role of RBI
- Regulator and supervisor of the financial system: RBI sets the rules and regulations under which Indian banks and financial systems must operate. The idea is to run the banks and financial system so efficiently that public trust in the system is maintained. When people feel confident about the financial system, it’s a win for RBI. How RBI ensures public confidence? By ensuring that the depositor’s money is safe with the banks, and all banking & financial functions are operating seamlessly as per rules. Read more on how RBI manages the financial system.
- Manager of Foreign Exchange: In India, all foreign currency flow must be done as per FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act). It is the RBI that ensures that transactions happen as per FEMA. The bigger role of RBI is in ensuring that external trade happens in a seamless manner. Whether the trader is a resident Indian or a foreign national, they must be able to deal in foreign exchange in an easy and transparent manner. Read more about Foreign Exchange Management by RBI.
- The Issuer of Currency: It is the responsibility of the RBI to print and issue new currency notes in India. It is also the RBI’s responsibility to exchange old or damaged notes for new ones. This way RBI can manage the availability of enough “good quality cash” needed in the market at a given point in time. Here, “cash” means both notes and coins. Read more about RBI’s role as an issuer of currency.
- Regulator and Supervisor of Payment and Settlement Systems:In India, all payments must be settles as per PSS Act, 2007 (Payment and Settlement Systems Act). It is the RBI who ensures that transactions happens as per PSS. In India there are several payments systems like ECS, Credit Card, Debit Card, RTGS, NEFT, IMPS and UPI. All these payments system are covered by PSS Act, 2007. The overall objective of RBI is to provide fast, safe and efficient payment system for the public. Efficient payment flows is one of the main confidence booster of the public in the Indian financial system. Read more here.
- Banker to Government: Like retail and commercial banks gives service to common public, RBI is the retail bank for the Government of India (GOI). RBI also acts as a merchant banker for the GOI. Read more about role of RBI as Banker to GOI.
- Banker to Banks: All Banks in India maintains an account with the RBI. They keep their statutory reserves and other deposits in this account. Hence, this way RBI also functions as banker to the banks. It is RBI’s responsibility to ensure inter-bank transactions. RBI can also lend money to banks as a special case. Read more about role of RBI as Banker to Banks.
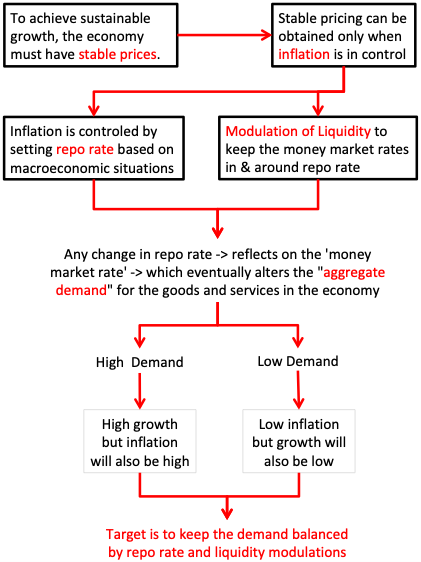
1. Function of RBI as a “Monetary Authority”
RBI functions as the “monetary policy maker”.
What is the objective of monetary policy making? To achieve the goal of “Price Stability” in the economy.
How RBI ensures price stability in Indian economy? By adopting an ‘inflation targeting” guidelines given to it by the government of India.
What is the current inflation target for RBI?
- Inflation (CPI): 4%
- Upper Limit: +4%
- Lower Limit: -2%
How RBI ensures that inflation remains within the prescribes limits? By the use of the following monetary instruments:
- Interest rates.
- Money Supply.
- Availability of Credit.
RBI “influences” the above three instruments to achieve the targeted inflation rate, and hence ensuring price stability.
Monetary Role of RBI in Modern Economy
Traditionally, RBI’s functions has been as follows:
- Regulate the issue of bank notes (& coins).
- Keeping Reservers.
- Ensuring Monetary Stability.
- Operating Currency & Credit System.
But over time, the functions of RBI has become more diverse and inclusive. In addition to the above roles, the following role has been made more prominent:
Maintain a balance between “price stability” and “economic growth”.
2. Function of RBI as “Manager of Financial System”
What is a financial system? The financial system of India is the environment under which the following institutions and instruments operate:
- Financial Markets,
- Financial Intermediaries, and
- Financial Assets.
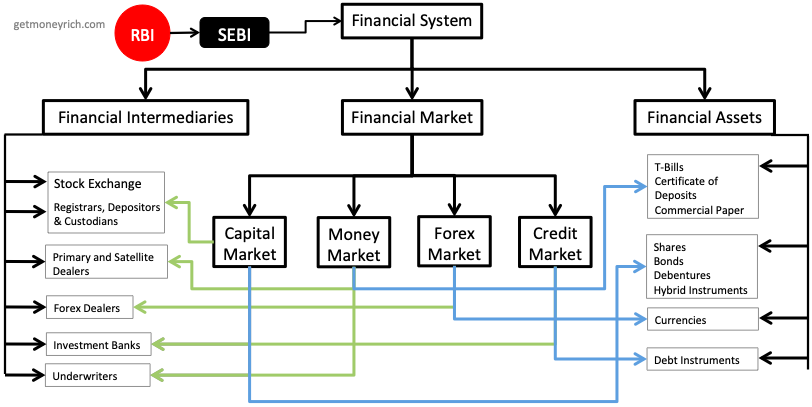
Financial system is a complex network of institutions and assets which work in tandem at a given point of time. It is RBI’s responsibility to lay-down the rules and regulations of how this network should work in India.
Once the system is in place and running, RBI their switches itself into the supervisory mode.
3. Manager of Foreign Exchange
All foreign exchange transactions are overseen and managed by RBI. Traditionally, RBI manages the foreign exchange by controlling its demand in Indian economy.
In the early days of Independent India, RBI was mainly regulating & deploying the inflow of foreign currency into India.
But in present times, RBI’s role as the Manager of Foreign Exchange is much more specific yet diverse. RBI regulates the foreign exchange flow in the country under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA).
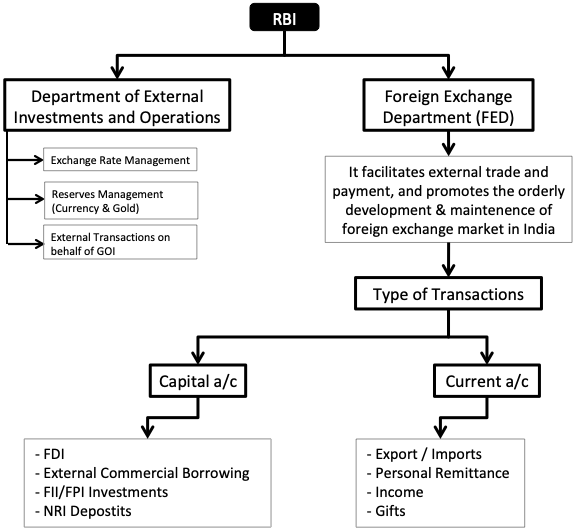
- Current Account Transactions: RBI’s role in current account transactions are limited. They cannot impose any restrictions directly. It is only the GOI which can do so (upon consultation with RBI). However, RBI’s intervention will be there as an exception on certain activities specified under schedule I, II & III.
- Capital Account Transaction: RBI specifies conditions of payments when transactions of capital account in nature (like FDI / External Commercial Borrowings / FII/FPI Investments, NRI Deposits etc).
- Exchange Rate & Reserves Management: This activity of RBI is done under a department called “Department of External Investments & Operations”. Their main function is management and investment of foreign exchange reserves (foreign currency and gold). Specific important is given to the safety, liquidity, and return aspect of the reserves.
4. Issuer of Currency
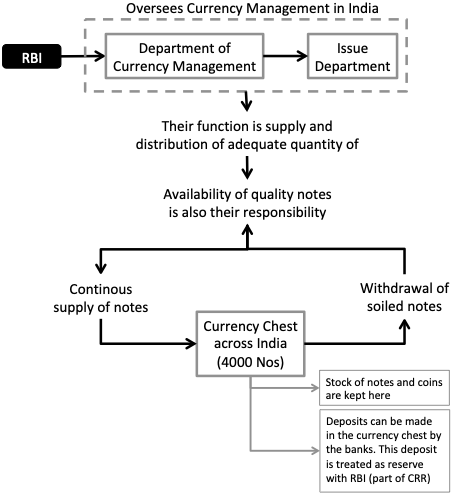
In the good old days, new currency issue was not as easy. Why? Because RBI used to follow a ‘proportional reserve system’. It means, for every new currency added to the economy, RBI must also proportionally increase its “reserves”. Here the reserves is foreign currency (mainly USD) and Gold.
But since 1956, ‘minimum reserve system’ has replaced the old rule. As per this rule, RBI must maintain a minimum reserves of Rs.200 Crore (Gold Rs.112 Crore). Once this minimum reserve is maintained by RBI can issue any number of notes.
The current level (June’2019) of foreign exchange reserves with RBI is Rs.29.4952 Lakh Crore (compared to Rs.200 Crore). In July’2015, foreign exchange reserves with RBI was Rs.19.2389 Lakh Crore. So it is clear that RBI is not just incessantly issuing Rupees. It is also proportionally increase the reserves.
5. Manager of Payment and Settlement Systems
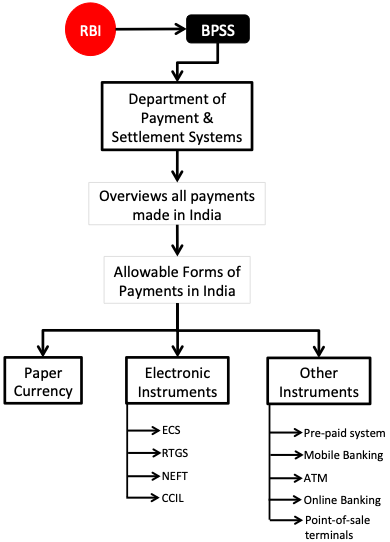
RBI is the only authority which can develop the nations payment system. These payment systems must be safe, secure, and efficient.
There is a BOARD (BPSS) which is responsible for the overall regulation and supervision of payments & settlement systems in India. BPSS is headed by the Governor of RBI.
In India, all money transactions are governed under an act called “Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act)”. BPSS takes all its decisions in accordance with this act.
There is a department in RBI called “Department of Payment and Settlement Systems” which takes direction from BPSS and executes decisions.
6. Banker to Government of India
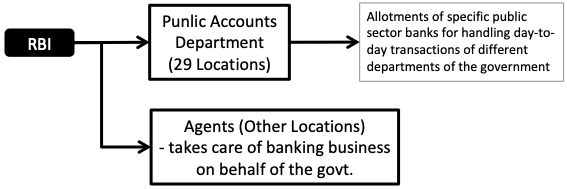
RBI is obliged to do all banking transactions on behalf of Central and State Governments of India.
In the bankers role to the government, RBI takes care of the following:
- Money,
- Remittance,
- Exchange,
- Banking transactions, and
- Management of public debt.
In lay man terms, specific activities of RBI are be as follows:
- Role as a banker:
- RBI pays and receives money on behalf of the government.
- It float loans on behalf of government.
- Issue Advances to government (both interest and non-interest bearing).
- Portfolio Manager:
- Invests surplus cash of the government.
- Advisor:
- Acts as one on monetary and banking related subjects.
7. Banker to Banks
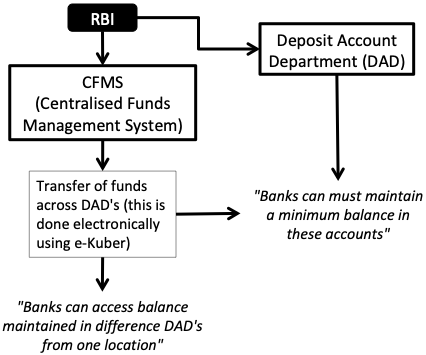
Banks are required to keep a minimum cash reserves with RBI. Hence, every bank has one account with RBI.
The accounts with RBI is also used for the following purposes:
- Setting inter-bank transactions.
- Clearing money market transactions.
- Buying/selling of securities.
- Buying/selling of foreign currencies.
RBI work as a ‘common banker’ for all banks. This facilitates the banks in the following ways:
- Smooth and efficient transfer of funds (between banks).
- To make payments on behalf of one bank to other.
- To receive funds on behalf of one bank from other.
In addition to above, RBI can also provide short term loans and advances to the banks
Suggested Reading:
