It’s the price volatility that makes stock investing so risky. But why does stock price fluctuate at all?
There can be several small and big reasons for the price volatility. But the main thing that triggers all price volatility is demand and supply of stocks.
When a stock’s demand is low (more sellers than buyers), its price will fall. When a stock’s demand is high (less sellers than buyers), its price will rise. So basically, it is the change in demand that triggers all stock price fluctuations.
So as an investor, if we can comprehend what factors influence stock’s demand, we can almost figure out why does stock price fluctuate.
Let’s delve slightly deeper into the economics of demand-supply-price relationships to understand how demand influence price.
Demand-Supply-Price Relationship
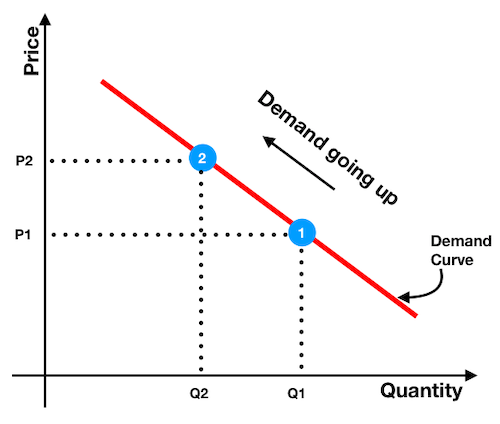
What we can understand from the above infographics? We will use a hypothetical example to understand it:
At point number one (1), supply of shares is Q1 and its price is P1. At this point this share was trading for few days. We can say it found its equilibrium at point 1.
Then the company declared that its profit has risen by 5% in the last quarter. This triggered the demand for its shares. This surge in demand is shown by the point two (2).
This is important to understand. When demand for the share shift from point 1 to 2, there is a simultaneous shift on the quantity axis from Q1 to Q2.
How this happened? Initial increase in demand sucked shares out of the market in short time. This created a supply deprived condition in the market (Q2 < Q1).
Hence how the market adjusted for this change? The stock price went up.
This explains why increase in demand, pushes the price of shares up.
Having said that, I would also like to bring this to table that comprehending stock’s price volatility is a tough ask. Even experts find it tough to judge and forecast price movements. So if you are not able to do it, do not blame yourself.
If stock price is so tough to predict, then how technical analysts give short term trading advices?

This is a very valid question. The whole stock trading business is based on “stock price momentum” model.
Does these people (traders) really know which way the price is going to go? Yes and No.
Yes because traders can sometimes be right. But again, its a guess work on their part. Expert traders study stock price movements very closely. Much closer than you and me will ever do.
When price movements are watched so closely, a trend begin to form. Stock traders place their bets based on the trends.
But stocks do not always follow their trends. Hence I said that, forecasting price is a guess work.
For investors, more important is to know what factors influence stock price. Instead of spending time on studying price patterns, better will be to study stock’s fundamentals and macro-economics. Why?
Because these are the two most important factors which ultimately influences the demand pattern for the stocks.
Let’s read more to understand…
Factors influencing demand pattern of stocks…
Stocks price fluctuate due to change in their demand. What influences demand?
- Internal Factor: Stock’s Business Fundamentals.
- External Factor: Macroeconomics.
What I mean by internal factors? Stock’s business fundamentals like its sales, profit, net worth, assets, profitability etc are things which are in control of the company. Improvement in these factors will eventually push its share price up in the stock market.
What I mean by external factor? Macroeconomic factors like economic activity, GDP growth, interest rates, inflation, currency valuation etc, are something which is not in control of the company. They have to live with it.
But changes in these factors eventually effects the performance of the company, and hence its share price in the market.
Broadly speaking, it is these internal and external factors which plays a major role in stock price fluctuations.
I am not talking about daily price movements. They are also caused by demand-supply imbalance. But daily movements are small, may be in fraction percentage points. Hence it will not be effective to go into details of such small movements.
What will discuss here are the major corrections (or up-trends), and what cause them to happen…

#1. Stock’s Business Fundamentals…
Investors expect stocks price to rise continuously. At least the trend should be up in the longer term. How this will happen?
Price will move up only if the business fundamentals will support its cause. No matter how healthy are the macroeconomics (external factors), they will prove ineffective till the underlying business of the stock is strong.
Strong underlying business means what?
- High net worth,
- Low debt,
- High profitability,
- Robust growth, and
- Strong liquidity position.
How these factors help? All these factors together contribute towards higher profits.
Companies whose profit grow with time, will surely see its price moving up. But as an investor we must understand few details related to profit.
There are two types of absolute value of profit that we shall be concerned about:
- Profit After Tax (PAT).
- Earning Per Share (EPS).
Over a period of time, these are the two most important factors which directly influences the stock price.
Lets start with PAT first…
#1.1 Profit (PAT)…
Companies profits has a strong influence on market price of its stocks. When profits will grow, its market price will also grow. When profits will fall, its market price will also fall.
So is it sufficient to analyse last five years profits of company and take a buying decision? No. Why? Let me give you an example.
A company ABC reported its net profit (PAT) as below:
- Rs.1,000 Crore in financial year 2015-16.
- Rs.1,200 crore in financial year 2016-17.
- Rs.1,440 crore in financial year 2017-18.
What we can understand from the above values? There is a clear growth trend. Uniform growth rate of PAT at rate of 12.9% p.a. in last 3 years.
This is a first clear sign that the stock’s underlying business is strong. But it is very important for investors to dig further into the financial reports.
Stopping at PAT level may lead to judgement errors. How? Let’s read more…
Even though the PAT of ABC is growing, but surprisingly, in the same period (3 years) market price of ABC was falling.
- Rs.400 in FY 2015-16
- Rs.380 in FY 2016-17.
- RS.362 in FY 2017-18.
How it is possible? Even though the company is increasing its net profits @ 12.9% p.a but market price of its stocks is still falling. What is the problem?
To understand this, let’s see the share price formula…
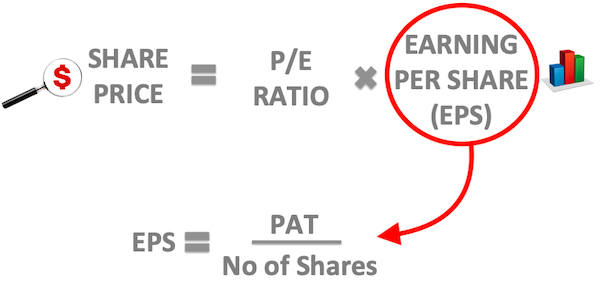
#1.2 Share Price Formula…
We all know this formula, right? This formula does not use PAT directly. It has a shade of PAT, but in form of EPS.
As per this formula, a share price is a multiple of P/E times its EPS.
What is P/E? Price Earning Ratio. Under normal times, stocks tries to hold its P/E levels. What does it mean?
If there are no major good news or bad news effecting the companies business, its stock tries to hold its P/E levels. For simplicity, let’s assume that P/E remains constant under normal business times.
So now in this situation, if a stock price has to go up, what must increase? EPS. What is EPS? EPS = “PAT” / “Nos of shares outstanding”. How EPS will increase?
PAT must increase at a rate faster than the growth of its nos of shares outstanding.
What does it mean? To understand this we must dig deeper into EPS…
#1.3 Earning Per Share (EPS)..
In our earlier example, we saw that though the company ABC was increasing its PAT @12.9% p.a. in last 3 years, but still its market price was falling. What could be the reason? EPS. How? Let’s see…
A company ABC reported its net profit (PAT) as below:
- Rs.1,000 Crore in financial year 2015-16.
- Rs.1,200 crore in financial year 2016-17.
- Rs.1,440 crore in financial year 2017-18.
But in the same period, the company was also issuing new shares in the market, thereby liquidating its EPS. How?
When the company issues new shares, the number of shares outstanding increases. This reduces the EPS (EPS = PAT / Nos of shares).
Lets see how new share issue effected ABC:
- 100 Crore Nos is shares outstanding in FY 2015-16.
- 125 Crore Nos is shares outstanding in FY 2016-17.
- 158 Crore Nos is shares outstanding in FY 2017-18.
We can see that the number of shares outstanding for ABC is increasing at a rate of 16% p.a. (faster than its PAT growth).
As a result the EPS of ABC is diminishing unlike its PAT:
- Rs.10/share EPS in FY 2015-16.
- Rs.9.6/share EPS in FY 2016-17.
- Rs.9.1/share EPS in FY 2017-18.
As company is liquidating its earnings by issuing more share in the market, its EPS is falling. The impact of EPS is direct on market price of its stocks.
One of the strongest business fundamental that effects market price of stock is its profits. But don’t let yourself get mislead by the term profit.
What an investor should see is not only profit (PAT) but also EPS & EPS growth.
When it comes to share price trend, nothing has more influence on share price than its underlying EPS trend.
Though “shares price growth” can also “outperforms their EPS growth rates”, but such instances are rare.
#2. Macroeconomics…
Till now what we have seen are the causes effecting share price, originating from within the company.
But companies cannot run in isolation from the rest of the world. There are macroeconomic forces which also influences the performance of the company, and hence its share price.
What are the main macroeconomic factors which has major influence on stock price fluctuations?
- Interest Rates.
- Gross domestic product GDP).
- Inflation.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Money Supply.
- Stock Market Index.
- Industry/Sector’s Health.

Allow me to explain few external factors which effects stocks price.
#2.1 Interest Rates
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has control on the interest rates. They can increase or decrease the interest rates to stimulate the economic activity in the country. When interest rates rise, companies will take less loan. Hence their performance will go down and vice versa. Low performance means, less profits (EPS). This will pull its share price down.
#2.2 GDP Growth
If the economy of the country is booming (fast GDP growth), it will also reflect in the price of the shares. Similarly, when GDP growth slows down, it will negatively effect the share price. Why? Because high growth rates are an indicator that the profits (EPS) of good companies will also increase with time. Higher profits eventually leads to higher share price.
#2.3 Inflation
When inflation is high, price of goods and services rise faster. Consumer show resistance to price rise, as a result sales of company falls. Low sales means lower profits. Moreover, to control inflation, RBI increases the interest rates. This further effects the business (see point #2.1 above). So, sustained high inflation rates are detrimental to share price in medium to long term.
#2.4 FDI
In June’2018, share price of Idea Cellular rose by approximately 2% in one day. Why? Because of the announcement by the Indian Government that 100% FDI is allowed in Idea type telecom business. Due to this rule, Vodafone’s goal of acquiring Idea Cellular became clear. As Vodafone is a telecom giant, hence the share price of Idea rose, taking it as a good news.
#2.5 Money Supply
What is money supply? Total money in circulation in India at a given point in time. It is estimated that as on Dec’18, total money supply (M3) in India was Rs.1,45,985 Billion. In Nov’18 this value was Rs.1,45,447 Billion. So, between Nov & Dec, money supply increased. It means, people had more money in hand for spending. When this happens, it is observed that people pour in more money in equity. Why? Because of the history of equity, it gives higher returns than debt based options. More money in equity, means higher share prices.
#2.6 Stock Market Index
When the main stock market indices (like NSE and BSE) are going up, price of other stock’s will also follow this path. The performance of the stock market index is generally influenced more rapidly by the external stimulus (like inflation, interest rates, etc).
#2.7 Sector / Industry
All stocks operates in their own sector/industry. Like DLF operates in real estate sector. TCS operates in IT sector. Ten years back, the real estate sector was booming in India. This effect was also seen in the stocks operating in this sector (like DLF, Unitech etc). But today this sector is going sluggish. No stock can perform well if its sector is not healthy. A weak sector eventually pulls the price down of its stocks as well.
Conclusion…
Stock price fluctuate due to demand-supply imbalance. The factor which influence demand is companies fundamentals.
Stock price may also fluctuate due to outside forces. Example: 2008-09 debt crisis originating in USA pulled stocks down of the whole world.




