Dividends are a golden stream of passive income. Hence dividends represent itself as a rewarding aspect of stock ownership. Dividends are the portion of a company’s profits distributed to its shareholders. It is the measure of a tangible return on investment. Dividends are financial rewards, distributed regularly by mature and profitable companies. In this way, dividend also becomes one indicator pointing towards large quality companies.
For investors, dividends serve as a cornerstone for investors seeking not just capital appreciation but a consistent income stream.
I consider dividend investing as my strategic way to unlock wealth over time. Why over time? Because a stage comes when our stock portfolio can start yielding returns of 6-7% per annum from dividends alone (check this case study).
In stock investing dividends serve a dual role for its investors. It serves as a source of immediate income and also as a testament to a company’s financial strength. Unlike market fluctuations, dividend income can provide reliable income, irrespective of market conditions. This kind of reliability is particularly crucial for risk-averse investors who like predictable cash flows.
One of the pivotal aspects of dividend investing is selecting stocks from companies with a proven track record of consistent dividend payments. These companies are known for increasing dividend payouts showcasing financial stability and management’s commitment to shareholder value.
Dividend focus is a way how investors can position themselves to benefit from both the immediate returns and the potential for higher future payouts.
In the journey towards long-term wealth growth, strategic dividend investing is our reliable companion. Let’s unravel the intricacies of strategic dividend investing, a pathway to financial prosperity.
Topics
Point #1. Understanding Dividend Investing
#1.1 Definition of Dividend Investing
Dividend investing is a financial strategy where investors prioritize stocks that offer regular and consistent dividend payments.
Unlike traditional stock investing, where the primary focus is on capital appreciation, dividend investing places a premium on generating steady income streams. This approach views dividends as bonus returns. There are two components of a return, dividend and price appreciation, building the overall return of a stock. The dividend investing strategy puts more weight on the dividend component.
Dividend-focused investors seek out companies known for distributing a portion of their net profits to shareholders. This distribution is usually paid in the form of cash. Some companies can also opt to pay their shareholders dividends in the form of bonus shares.
The allure of dividend investing, for shareholders, lies in its potential to become a reliable alternative income stream. It can provide the investor with financial stability, especially during market volatility.
#1.2 Key Metrics: Dividend Yield, Dividend Growth Rate
Two key metrics play a pivotal role in dividend investing: Dividend Yield and Dividend Growth Rate.
- Dividend Yield: It is the annual dividend income represented as a percentage of the stock’s current market price. It is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock’s market price. The higher the dividend yield, the more substantial the return on investment for the investors.
- Dividend Growth Rate: This rate reflects the increase in a company’s dividend, per annum, over time. A consistent and positive growth rate signals a company’s ability to enhance shareholder value. How? By ensuring a steady growth of dividend payouts.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the benefits, risks, and strategic considerations that define a dividend-focused investment approach. We’ll shed light on how it can be harnessed for long-term financial success.
Point #2. Benefits and Risks of Dividend Investing
#2.1 Benefits
- Regular Income Stream: One of the primary attractions of dividend investing is the assurance of a regular income stream. Investors in dividend-paying stocks receive periodic payments (generally once a year or every quarter). This predictable cash flow is particularly appealing to those seeking to supplement their income. Hence, dividend income can be a vital source of income during one’s retirement life.
- Capital Appreciation: While dividends offer a steady income, dividend-paying stocks also have the potential for capital appreciation. Investors can benefit from the dual advantage of earning income through dividends and witnessing capital growth over time. This combination provides a comprehensive approach to wealth building.
- Lower Volatility: Dividend-paying stocks often exhibit lower volatility compared to non-dividend-paying counterparts. How? Because in tough times like (the 2008 crash or Covid crash), investors tend to hold on to high-dividend paying stocks. The attraction for a steady income stream, provided by dividends, acts as resistance to sell.
#2.2 Risks
- Market Risks: Dividend stocks are not immune to market risks. The market price of these stocks will be influenced by broader market trends and sentiment. For example, in the 2008 crash and COVID-19 crash, the price of all stocks took a beating. When such events occur, both capital appreciation and dividend income are affected.
- Economic Downturns: When a business faces a financial crisis, it will struggle to maintain its profit. It will eventually affect the dividend payments as well. In most cases, there is a direct effect on dividends when the net profits of companies rise or fall. We saw this effect curing the COVID-19 crash.
- Interest Rate Risks: In a rising interest rate environment, fixed-income investments become more attractive. Hence, big investors divert their funds to options like bonds, bank deposits, etc. This shift, away from stocks, can lead to a decline in stock prices impacting both capital appreciation and dividend yields. Read about debt mutual funds.
Dividends do offer stability and income. But as an investor, we must be vigilant and aware of the potential risks that are inherent in all stocks.
In the subsequent sections, we’ll explore different types of dividend stocks. This information can help us further fine-tune our dividend investing strategy.
Point #3. Types of Dividend Stocks
#3.1 Dividend Blue Chips
Blue Chip companies, often represent stable and well-established businesses. They have demonstrated resilience and comparative stability through various market conditions. Among these blue-chip companies, we must look for those elite stocks that have consistently paid dividends in the past. The past period can be as long as 10 to 20 years.
Investors whose focus is on maximizing their dividend yield in times to come (like in the next 10-20 years), can think of including dividend blue chips in their stock portfolio.
#3.2 High Dividend Yield Stocks
High Dividend Yield Stocks are characterized by their high dividend payouts relative to their stock prices.
While the attraction for high dividend yield is understandable, it is also crucial to evaluate the sustainability of those yields. Currently (in Jan-2024), below are a few stocks that are currently yielding very high yields. But the question is, are these dividend payouts sustainable? In most cases, it is not.
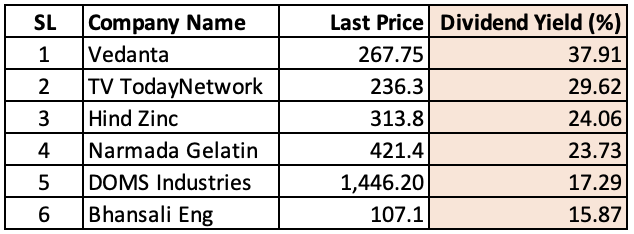
Companies offering such high yields will surely lower their payouts in the future. They may also sometimes face challenges to maintain the financial health of the underlying businesses with such high payouts.
My thumb rule is that, if the dividend yield at current prices is beyond 10% levels, I do a more detailed analysis of their revenue, profit, and payouts. The idea of such analysis is to establish if the company can afford such payouts sustainably.
For example, Vedanta has been making less net profits and distributing more dividends to its shareholders. This simple table will highlight that such acts of kindness cannot continue. It is bad for their business in the long term.
| Vedanta | Mar-23 | Mar-22 | Mar-21 | Mar-20 | Mar-19 |
| Net Profit (PAT) | 14,506.00 | 23,709.00 | 15,033.00 | -4,743.00 | 9,698.00 |
| Dividend | 37,572.00 | 16,681.00 | 3,519.00 | 1,696.00 | 8,411.00 |
| Dividend as % of PAT (Payout Ratio) | 259% | 70% | 23% | -36% | 87% |
#3.3 Dividend Growth Stocks
Dividend Growth Stocks prioritize companies with a consistent history of increasing dividend payments over time. Investors gravitate towards these stocks not just for immediate income but also for the potential of higher future payouts.
The emphasis is on companies with a robust revenue, profit, and margin outlook. Such companies, if they are already paying dividends, are more likely to report sustained dividend growth. This approach aligns with a long-term wealth-building strategy.
#3.4 Value Stocks With Dividend Potential
Value Stocks that also pay dividends combine the principles of value investing with the added benefit of short-term dividend income. Mostly, investors invest in value stocks for long-term capital appreciation. However, buying quality dividend stocks at undervalued price levels can also render high yields.
These stocks may not always have the highest current yields. However, their intrinsic value and growth prospects position them as attractive options for times to come.
For me, a stock investor cannot miss buying value stocks that also pay dividends consistently.
Point #4. Factors to Consider in Dividend Investing
- Company’s Financial Health: Analyzing a company’s financial health is a fundamental step in dividend investing. Sound financials indicate a company’s ability to generate consistent earnings and pay consequent dividends. Key financial metrics, such as revenue trends, profit margins, and debt levels, offer insights into the company’s stability.
- Dividend Payout Ratio: The Dividend Payout Ratio is a crucial metric in dividend investing. It represents the proportion of profit a company distributes as dividends. A sustainable payout ratio ensures that a company retains enough earnings for future growth and unforeseen challenges. We as investors should favor companies with moderate payout ratios. Excessively high ratios are often unreliable and inconsistent.
- Dividend Sustainability: Factors influencing dividend sustainability include consistent cash flow and manageable debt levels. A profit-making company whose cash flow and debt are under control can afford to pay dividends regularly. We must look beyond current dividend yields and analyze if the company can (actually) afford dividend payments.
- Company’s Growth Potential: A company with strong growth prospects is likely to increase its profits. The profit growth eventually leads to higher future dividends and potential capital appreciation.
[Note: A company that is able to generate high Free Cash Flow (FCF) can pay regular dividends]
Point #5. Popular Dividend Investing Strategies
#5.1 Dividend Reinvestment
Dividend reinvestment can help us compound our wealth over time. Shareholders must make sure to reinvest the dividends back into additional shares of the same stock. If the same stock is looking expensive, one can buy an alternative value stock that also pays dividends.
This strategy will harness the power of compounding, allowing us to benefit from the compounding effect. This way, both the initial investment and subsequent reinvested dividends will grow with time.
Reinvestment of dividends is an effective strategy for long-term investors seeking to maximize the growth potential of their dividend portfolios.
#5.2 Dogs of the Nifty
The Dogs of the Nifty50 strategy involves selecting stocks from the Nifty Index (50 Stocks) with the highest dividend yields. The premise is to invest in well-established companies that have temporarily fallen out of favor.
Two quick ways to judge if the stock is currently out of favor is to look at its last 14-day, 30-day, and 90-day price trends. If there is a falling price trend, it becomes our first hint.
The second hint is the dividend yield metric. The price fall will result in higher-than-average dividend yields. So, we can invest in those Nifty50 stocks whose price is falling and current dividend yield is high (like above 2.5%).
People who are already following this strategy must also rebalance their portfolios. How to do it? By adding more stocks at those price levels where they are yielding higher dividends.
#5.3 Value Investing with a Dividend Focus
Value Investing with a Dividend Focus combines the principles of value investing with a specific emphasis on dividend-paying stocks.
Investors following this strategy seek stocks that are undervalued by the market but have the potential for future appreciation. Additionally, these stocks should offer attractive dividend yields.
By focusing on companies with strong fundamentals, consistent dividends, and potential for price appreciation, investors can make money in long term. This way, investors can aim to create a well-rounded portfolio that delivers both income and long-term growth.
Point #6. Tax Considerations in Dividend Investing
Dividend investing is a type of short-term fixed-income stream. Hence, it comes intertwined with the intricacies of taxation. Understanding the tax implications is also crucial for optimizing our returns.
Let’s see how the tax laws shape up the dividend yields and how we can navigate them for efficient gains.
#6.1 Taxation on Dividends in India:
- Ordinary Dividends: It is treated as income from other sources. Hence are taxed according to our individual income tax bracket. While no dividend distribution tax (DDT) is levied anymore, the onus of tax payment rests on the investor.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): The company or mutual fund deducts 10% TDS on dividend income exceeding Rs. 5,000. We can claim refunds if our actual tax liability is lower.
Is there a way to save income tax on dividend income from stocks in India? Unfortunately, there are no straightforward ways to fully avoid tax on dividend income from stocks.
However, if one is too worried about income tax, a better alternative is to invest in stocks through the equity mutual fund route. There, keep in mind that you “do not” opt for the dividend payout options. Here, make sure to stay invested for a very long term (like 5+ years). However, whenever the holdings are sold, long-term capital gain tax will be applicable. There is no way of avoiding it.
Point #7. Future Trends in Dividend Investing
Anticipating future trends is essential for investors seeking to adapt and thrive in changing environments. Here are key considerations for the future of dividend investing:
#7.1 Impact of Economic Changes
Economic changes can significantly influence dividend investing trends. Economic downturns, recovery phases, and periods of inflation can affect companies’ abilities to sustain and grow dividends.
Investors should remain informed about the macroeconomic indicators and RBI’s policies. This is essential to build along long-term dividend portfolio. The ability of a company to navigate economic changes often determines its resilience in sustaining dividend payments.
#7.2 Technological Advancements and Dividend Stocks
The rapid pace of technological advancements introduces a new dimension to dividend investing.
Companies at the forefront of innovation, particularly in technology-related sectors, may offer compelling opportunities for future dividend growth. Dividend investors should look beyond traditional sectors (like banking and utility) for dividends. We can explore technology-driven companies with robust fundamentals.
When I say technology companies I do not necessarily mean companies from the IT sector alone. Other non-IT companies are using technology to build a new market of their own.
Here are some exciting listed stocks in India, like Zomato and Paytm, that are leveraging technology to carve out unique market niches:
Fintech:
- PB Fintech (Policybazaar): A leading online insurance aggregator. It uses AI and big data to personalize recommendations and simplify the insurance buying process.
- Nazara Technologies: It is a diversified gaming and sports media company. It employs technology to build a strong presence in esports and mobile gaming.
- Pine Labs: It is a payment gateway and merchant solutions provider. It focuses on offline-to-online payments and digital credit solutions for small businesses.
E-commerce and Retail:
- Nykaa: It is an online beauty and personal care retailer. It also utilizes AI and data analytics for personalized product recommendations and customer engagement.
- Meesho: It is a social commerce platform. It connects small businesses and consumers through social media networks. Its prime focus is on Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Cartrade Tech: It is a leading online automobile marketplace. It uses technology to provide comprehensive information to potential car buyers. It gives virtual showroom experiences, and online buying options for cars.
Logistics and Mobility:
- Delhivery: It is a major player in the logistics space. It leverages technology for efficient route optimization, warehousing management, and last-mile delivery solutions.
- DroneAcharya Logistics: A pioneering drone delivery startup, aiming to revolutionize transportation in remote areas and challenging terrains.
- IdeaForge: It’s a drone tech leader. It has pioneered vertical-takeoff drones used in defense & civil mapping. They have a large deployment of indigenous drones in India and rank 5th globally in the dual-use category.
As these companies are very new, one must conduct a deep fundamental analysis before making any investment decisions.
#7.3 Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors
ESG considerations are gaining prominence in the investment landscape, influencing the choices of conscientious investors. The integration of environmental, social, and governance factors in dividend investing reflects a broader shift toward sustainable and responsible investment practices.
Companies with strong ESG practices are viewed favorably by investors who prioritize long-term sustainability and ethical business conduct. As ESG awareness continues to rise, it is expected to shape the future landscape of dividend investing, impacting investment decisions and corporate behaviors alike.
#8. Case Study
#8.1 INFOSYS:
Suppose an investor bought 1 share of Infosys in 2004 at Rs.4,939 each. In 2004, Infosys paid a dividend of Rs.129.42 per share. This amounts to a dividend yield of 2.62% per annum.
After 20 years (in 2023), after bonuses and stock splits, the shares holding increased from 1 to 16 numbers. As of Mar’23, Infosys pays a dividend per share of Rs.32.59 per share. This amounts to a dividend yield of 10.56% per annum.
In these 20 years, for our example investors, the dividend yield of Infosys has increased from a decent 2.62% to a fair 10.56% per annum.
[Please note that this yield the investor earns just by holding on to his stocks.]
| Description | Formula | Numbers |
| Total Shares Bought | a | 1 |
| Buy Price | b | 4939.69 |
| Dividend Per Share (2004) | c | 129.42 |
| Dividend Yield (2004) | d = c/b | 2.62% |
| Shares in 2023 | e | 16 |
| Dividend Per Share (2023) | f | 32.59 |
| Total Dividend | g = e * f | 521.40 |
| Dividend Yield (2023) | h = g/b | 10.56% |
#8.2 L&T:
Suppose an investor bought 1 share of L&T in the year 2004 at Rs.587 each. In 2004, L&T paid a dividend of Rs.15.57 per share, amounting to a dividend yield of 2.66% per annum.
After 20 years (in 2023), after bonuses and stock splits, the shares holding increased from 1 to 6 numbers. As of Mar’23, L&T pays a dividend per share of Rs.18.25 per share, amounting to a dividend yield of 18.67% per annum.
In these 20 years, for our example investors, the dividend yield of L&T has increased from a decent 2.66% to an impressive 18.67% per annum.
[Please note that this yield the investor earns just by holding on to his stocks.]
| Description | Formula | Numbers |
| Total Shares Bought | a | 1 |
| Buy Price | b | 586.31 |
| Dividend Per Share (2004) | c | 15.57 |
| Dividend Yield (2004) | d = c/b | 2.66% |
| Shares in 2023 | e | 6 |
| Dividend Per Share (2023) | f | 18.25 |
| Total Dividend | g = e * f | 109.47 |
| Dividend Yield (2023) | h = g/b | 18.67% |
#8.3 Britannia:
Suppose an investor bought 1 share of Britannia in the year 2007 at Rs.1,620 each. In 2004, Britannia paid a dividend of Rs.15.57 per share, amounting to a dividend yield of 0.93% per annum.
After 20 years (in 2023), after bonuses and stock splits, the shares holding increased from 1 to 10 numbers. As of Mar’23, Britannia pays a dividend per share of Rs.56.76 per share, amounting to a dividend yield of 35.02% per annum.
In these 20 years, for our example investors, the dividend yield of Britannia has increased from a low of 0.93% to a very impressive 35.02% per annum.
[Please note that this yield the investor earns just by holding on to his stocks.]
| Description | Formula | Numbers |
| Total Shares Bought | a | 1 |
| Buy Price | b | 1620.80 |
| Dividend Per Share (2004) | c | 15.00 |
| Dividend Yield (2004) | d = c/b | 0.93% |
| Shares in 2023 | e | 10 |
| Dividend Per Share (2023) | f | 56.76 |
| Total Dividend | g = e * f | 567.65 |
| Dividend Yield (2023) | h = g/b | 35.02% |
Conclusion
Dividend-focused investing can be a lucrative strategy. However, the problem with this strategy is that it asks investors to look years ahead in the future. As current dividend yields are rarely encouraging, people mostly go for growth stocks as their preferred options.
However, people who want to benefit from both capital appreciation and short-term income should consider dividend investing as their preferred strategy.
In this article, we’ve discussed how current investors can implement this strategy to maximize their dividend income in times to come.
Have a happy investing.
Suggested Reading:



![Stock Investment For Beginners – A Detail Guide [India]](https://ourwealthinsights.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/Stock-Investment-for-Beginners-image.png)


