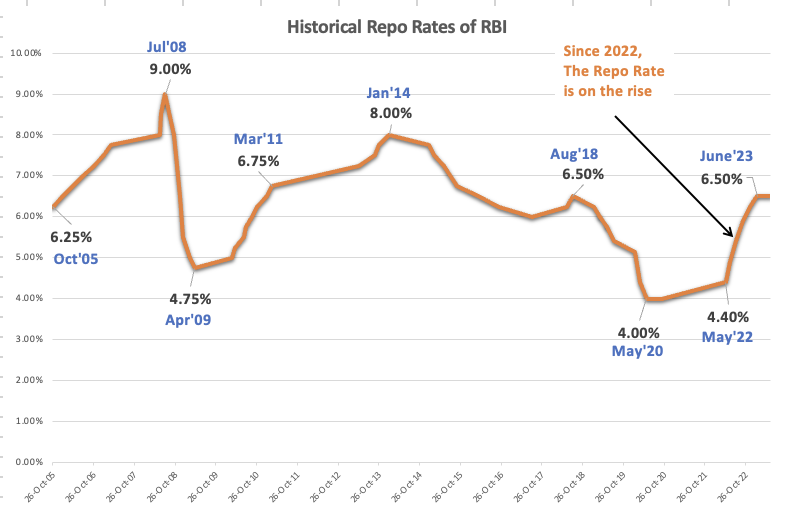
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raised the repo rate (Interest Rates) by 0.25% in Feb’23 (see repo rate history since 2005). This was the fifth repo rate hike since Oct 2020. The rising interest rates often have a negative impact on the stock market. They make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest, creating a liquidity crunch in the economy.
The impact of the rate hikes will vary depending on the sector and the company. Companies that are highly leveraged and rely on debt financing will be the most affected. These companies may have to cut back on their investments and operations, which could lead to lower earnings and stock prices.
The rate hikes are also likely to dampen investor sentiment. Investors may become more cautious and less willing to take risks, which could lead to a sell-off in the stock market.
However, the impact of the rate hikes is not only negative. Some sectors, such as Banks and NBFCs, could benefit from the higher interest rates. They will earn more money from lending. They will see their profits improve as their borrowers will pay higher interest rates on their loans.
Let’s get deeper into the basics of how the rising interest rates impact the stock market.
#1. Why Interest Rate (Repo Rate of RBI) is Rising?
After COVID-19, inflation is on the rise all over the world. All major economies of the world are impacted by the rising inflation scenario. Developed country like the USA and countries in the European Union was dealing with inflation at 1% or below levels. But post-COVID, the decades of low inflationary economy seem to have ended. Even the USA and UK are now dealing with 8% level inflation rates.
| Economies | Year-2020 | Year-2023 | Rise By |
| USA | 1.23% | 8% | 6.77% |
| UK | 0.99% | 7.92% | 6.93% |
| Germany | 0.14% | 6.87% | 6.73% |
| France | 0.48% | 5.22% | 4.74% |
| Italy | -0.14% | 8.20% | 8.34% |
| S.Korea | 0.54% | 5.09% | 4.55% |
| Japan | -0.03% | 2.50% | 2.53% |
| Australia | 0.85% | 6.59% | 5.74% |
| India | 6.62% | 7.44% | 0.82% |
| Brazil | 3.21% | 9.28% | 6.07% |
| South Africa | 3.21% | 7.04% | 3.83% |
| Indonesia | 1.92% | 4.21% | 2.29% |
| Malaysia | -1.14% | 3.38% | 4.52% |
The USA and major economies of the European Union have seen a stubborn rise in inflation. Hence, in those countries, the focus came on the interest rates. Though India is not as affected by the growth in inflation rates, being a fast-developing country, it can quickly go off limits. Hence, the Indian government has kept the Repo Rates tight since October 2020.
The repo rates are taken as a reference to decide the interest on all types of bank loans. In a rising repo rate scenario, bank loans charge high-interest rates. Moreover, repo rates are also a basis for discount rates of future cash flows. It is used to calculate the present values of all future cash flows.
This is the reason why, when interest rates are rising in an economy, it impacts the related stock market.
There is a famous quote of Warren Buffett on this subject. “The most important item over time in valuation is obviously interest rates. If interest rates are nothing, values can be almost infinite. If interest rates are extremely high, that’s a huge gravitational pull on values.“
– Warren Buffett
Central Banks of all major economies of the world are raising interest rates to tame inflation. However too high rates can have a negative effect on the GDP growth.
So, as a stock market investor, we must know that there must be a balance between inflation, interest rates, and the GDP growth rate. In a falling interest rate scenario, a quick bull run is common. But in a balanced economy, a slow but steady bull run can be achieved.
This calls for another question:
#2. How The Rising Interest Rates Impacts The Stock Market?
When we say stock market, we are either talking about the major indices like Nifty 50 or Sensex, or the individual stocks. When interest rates are on the rise, it generally affects the stocks and indices negatively.
Generally speaking, there could be four ways in which a rising repo rate can affect the stock market as a whole.
Four Factors
- Companies Make Less Profits: Capital-intensive companies who rely more on debt to finance their working capital and growth, generally have a heavy loan book. When interest rates are on the rise, the interest expense of these companies increase. This in turn decreased the company’s absolute profit and profitability. The falling profits and margins work as a drag on their stock’s price. The majority of companies are affected by rising interest rates, hence the stock market as a whole gets negatively affected.
- Investors Give Less Valuation to Company’s Stocks: Value investors value stocks by calculating the present value of their future cash flows. This is done by discounting future cash flows using a discount rate. The discount rate (WACC) increases when the repo rates rise. This leads to a lower present value of stocks leading to it’s price fall.
- Alternative Investments Look Dearer: Rising inflation hence interest rates cause devaluation of currency. During a high inflationary environment, investors invest more in alternative investments like gold and real estate. Furthermore, when interest rates are rising, fixed instruments like bonds and deposits also fetch better returns. Hence, investors shift there as well.
- Negative Sentiment: Generally speaking, people do not like rising interest rates. Why? Because it makes debt costly, liquidity is restricted and hence people can spend less. Moreover, rising rates lead to things becoming costlier. It creates a negative sentiment among people. In such a situation people tend to invest less leading to negative movements in the stock market.
These four reasons caused by rising interest rates negatively affect the stock market.
It is clear that rising repo rates are neither liked by people nor the corporates. But are all companies equally impacted by the rising repo rates? Which companies are most and least affected:
#3. Which companies are most and least affected by rising interest rates?
The best performers:
Banking stocks and NBFCs are positively affected by the rising repo rate scenario. As per the business model of these financial stocks, they lend money to society and make money. In a rising interest rate scenario, they can collect more due to elevated interest rates. It means some companies are happy when RBI starts to hike the repo rates. Hence, in the rising interest rates regime, banking and NBFC stocks become top performers while other stocks are struggling.
Blue chip stocks that pay consistent dividends are preferred during such times. During times of negative sentiments, investors try to play safe. They keep their funds safe in a bank as fixed deposits or simply as cash. If at all they want to venture into equity, they will prefer stable, established companies. Dividends paid by such companies become like icing on the cake for the investors.
Companies operating in the healthcare sector perform better (relatively) in a negative environment. No matter how high are the interest rates, people generally do not compromise when health is calling. In a situation when all companies are doing badly, generally, hospitals, labs, pharma stocks, etc. do relatively well.
The worst performers:
New-age growing companies are most affected by the rising interest rate conditions. These are companies that are currently thriving on debt to fund their fast growth leading to market capture. To an extent, such companies are dependent on debt even to finance their working capital. These companies mostly report losses currently. Hence, rising interest rates make their interest outgo even higher leading to more losses.
Moreover, investors value such companies (currently loss-making) by assuming that they will turn profitable in years to come. Such future cash flow assumptions are heavily discounted. Rising interest rates lead to even stricter discount rates leading to less valuation. Hence, investors may sell such stocks.
This is the reason why such companies often want Private Equity funding which are interest free. However, not all companies can secure PE funds.
Even if these companies are making profits, their shares trade at very high price-to-earning multiples. When interest rates are rising, investors may not buy shares at such high multiples leading to more selling.
Hotels, restaurants, and companies in the entertainment industry are also negatively affected. In the rising rate scenario, people and corporations are spending less. This happens as debt becomes costly and negative sentiments also prevail. This badly affects the performance of such companies.
Conclusion
When inflation is rampant, RBI tweaks the repo rate (interest rates) to control inflation. However, this method to keep inflation well within its peak can harm the stock market. During such times, growth stocks, new-age startups, and consumer spending-dependent industries face detrimental outcomes.
Generally speaking, a majority of the stock market is facing downside pressure when interest rates are rising. Hence, it becomes important for investors to pick those sectors, industries, and specific companies that can survive the wrath of such times.
The legendary investor Warren Buffett points strongly towards companies that can survive the tough times of the rising rate regime. He says, I will quote:
“When interest rates are rising, it’s important to focus on businesses that have pricing power and can generate cash flow even when rates are higher.”
– Warren Buffett
Have a Happy Investing.
Suggested Reading: